RNA binding protein mapping: RIP, CLIP, HITS-CLIP, PAR-CLIP
(Restore this version)
Modified: 10 May 2019, 12:15 PM User: Alice Audisio →
PAR-CLIP
Photoactivatable-Ribonucleoside-Enhanced Cross linking and Immunoprecipitation
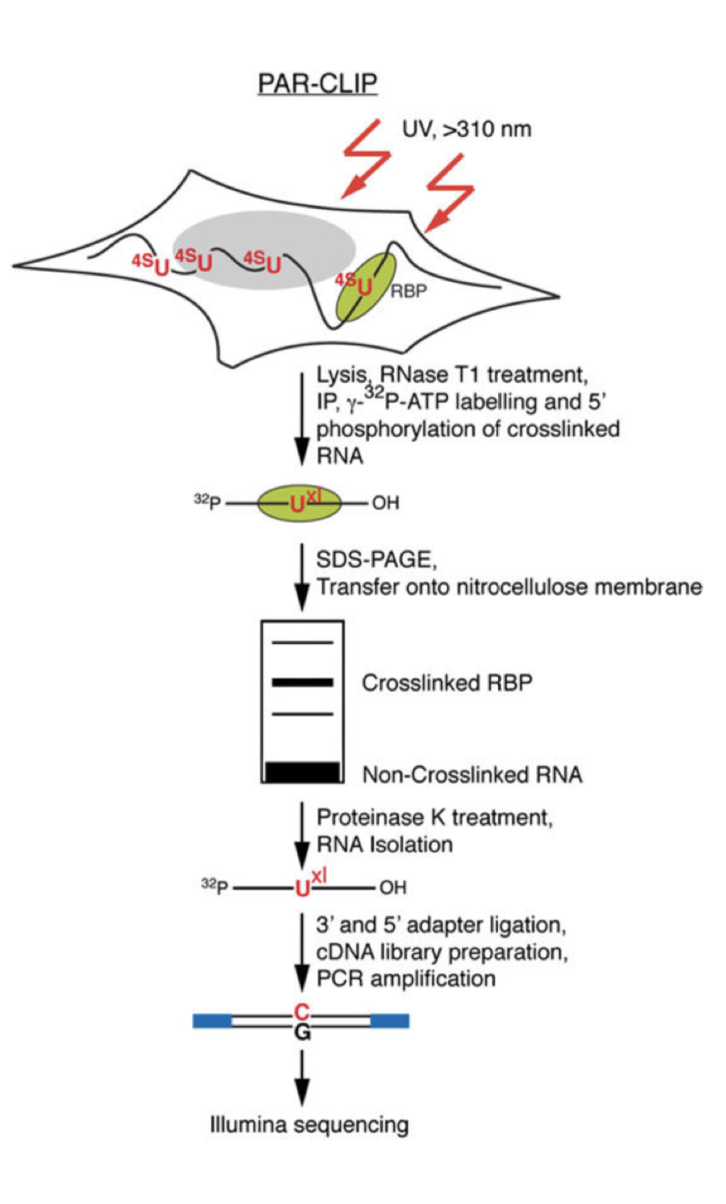
PAR-CLIP is a method for identifying RBP binding sites on target RNAs with nucleotide-level resolution.
It's applicable to any protein that contact directly RNA, including RBPs that are predicted to bind in a sequence- or structure- dependent manner at discrete RNA recognition elements (RREs), and those that are thought to bind transiently, such as RNA polymerases or helicases.
In PAR-CLIP are
Important features :
Photoactivatable ribonucleosides, usually the 4-thiouridine (4SU) and more rarely the 6-thioguanine (6SG), are incorporated into nascent RNA transcripts.
- The labeled RNAs are excited in living cells with UVA or UVB light (>310 nm) and yield photoadducts with interacting RBPs, that a represents an increased cross-linking efficiency compared to 254 nm CLIP
- A characteristic mutation (T-to-C for 4SU and G-to-A for 6SG) is introduced during reverse transcription at the position of cross-linking. This mutation permits the localization the sites of RNA–RBP interaction with nucleotide resolution and enables the user to computationally remove the ubiquitous background of co-purifying fragments of cellular RNAs that otherwise may be misinterpreted as signal
Method :
- Expanding Cells
- UV-cross-linking
- Cell Lysis and RNase T1 Digest
Immunoprecipitation and Recovery of Crosslinked Target RNA Fragments
- Preparation of Magnetic Beads
- Immunoprecipitation (IP), Second RNase T1 Digestion, and Dephosphorylation
- Radiolabeling of RNA Segments Crosslinked to Immunoprecipitated Proteins
- SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis, Transfer, and Recovery of RNA from Nitrocellulose Membrane
- Proteinase K Digestion
cDNA Library Preparation and Deep Sequencing
- 3′ Adapter Ligation
- 5′ Adapter Ligation
- Reverse Transcription
- PCR Amplification
- Optional: Determination of Incorporation Levels of 4-Thiouridine into Total RNA
PAR-CLIP Analysis
- Illumina sequencing : >200 million sequence reads per sample
- Sophisticated approaches to identify binding sites
- Calculation of the common sequence motifs of the RRE using one of the programs developed for the analysis of transcription-factor binding sites on DNA ( MEME, MDScan, PhyloGibbs, cERMIT, Gimsan)
Generally, the analysis of the sequence reads begins by alignment to the genome, allowing for at least one error (substitution, insertion, or deletion) to capture cross-linked reads with cross-linking-induced mutations.
Next, overlapping sequence reads are grouped, taking into account the frequency of cross-linking-induced mutations.
The frequency of the T-to-C mutations (or G-to-A mutations when using 6SG) allows ranking of groups to predict those interactions with the highest functional impact.
It's possible to found additional and interesting informations on this video