Transcription Factor mapping and prediction
Table of contents
1.1.1. Cell type specific Dam-ID :
1.1.2. Targeted DamID :
1.1.3. FRT/FLP-out DamID :
2. [edit]
Return to index
List of subjects:
1. TF binding site mapping genome-wide
2. TF sequence element prediction
3. biochemical determination of binding sequence (e.g. SELEX)
4. Activity assays for TFs
5. Dam-ID ( DNA Adenine Methyltransferase Identification )
(Samar El Sherbiny)
1. TF binding site mapping genome-wide
The identification of transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) is an important initial step in determining the DNA signals that regulate transcription of the genome. We have different techniques able to identify this TFBS:
a. ChIP-seq
ChIP-seq is a technique that combines two aspects: chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing. It's a powerful method for identifying genome-wide DNA binding sites for transcription factors and other proteins. Following ChIP protocols, DNA-bound protein is immunoprecipitated using a specific antibody. The bound DNA is then coprecipitated, purified, and sequenced.
Advantages:
- We can analyze the entire genome;
- It reveals gene regulatory networks in combination with RNA sequencing and methylation analysis;
- It offers compatibility with various input DNA samples.
ChIP-seq workflow:
The first part is the Chromatin immunoprecipitation or library prep:
- Chromatin is crosslinked in order to fix all the interactions with proteins. Than it is fragmentated, for this step we can use different methods, but the most used is sonication.
- Than we have the enrichment, specific antibodies for the protein of interest are added to the sample in order to perform the immunoprecipitation.
- At this point we can revert the crosslinking in order to obtain the DNA that will be purified. In order to perform NGS for the following step, that is sequencing, we will need also additional steps like end repair, phosphorilation, A-tailing, logation to the adapter and finally our sample will be ready for the sequencing.
The second part is the sequencing:
Before sequencing the fragments are amplyfied thanks to PCR and than we can have the sequencing, usually performed with NGS. In order to understand better all the steps of NGS sequencing i put a video from Illumina web site: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=290&v=fCd6B5HRaZ8
After sequencing the third part of ChIP-seq technique is the analysis of data:
Basically we obtain reads, they are small fragments that we can obtain after the sequencing. All the reads are mapped on the reference genome and we can see an enrichment in some spots: they are called peaks and from this output we can assume that the most enriched sites are with high probability the sites in which we have the binding between the transcription factor and the DNA. An important step in order to obtain data that are precise, is to estimate and eliminate the background. If we want to know the motif we need to perform the peak calling and peak annotation. Usually the binding site is around the center of the peak. To calculate the motif we need bioinformatic tools and specific algorithms.
b. ChIP on chip
ChIP-on-chip is a technology that combines chromatin immunoprecipitation with DNA microarray. It used to investigate interactions between proteins and DNA in vivo. Specifically, it allows the identification of the binding sites, for DNA-binding proteins on a genome-wide basis. This assay can be divided into two main parts:
- Wet-lab step
Basically the first step consist in the chromatin immunoprecipitation, like the one of ChIP-seq, but after the purification of DNA we have the labeling with a fluorescent probe. Finally, the fragments are poured over the surface of the DNA microarray, which is spotted with short, single-stranded sequences that cover the genomic portion of interest. Whenever a labeled fragment finds a complementary fragment on the array, they will hybridize and form again a double-stranded DNA fragment.
- Dry-lab step
The array is illuminated with fluorescent light, the probes on the array that are hybridized to one of the labeled fragments emit a light signal that is captured by a camera. Than the captured fluorescence signals from the array are normalized. At this point it is possible to perform the analysis of the enriched regions and identify the binding sites.
c. ChIA-PET
Chromatin Interaction Analysis by Paired-End Tag Sequencing is a technique used to determine de novo long-range chromatin interactions genome-wide. In this method, DNA-protein complexes are crosslinked and fragmented. Specific antibodies are used to immunoprecipitate proteins of interest. Two sets of linkers, with unique barcodes, are ligated to the ends of the DNA fragments in separate aliquots, which then self-ligate based on proximity. The DNA aliquots are precipitated, digested with restriction enzymes, and sequenced. Deep sequencing provides base-pair resolution of the ligated fragments. So we can say that ChIA-PET can be used to identify unique, functional chromatin interactions between distal and proximal regulatory transcription-factor binding sites and the promoters of the genes they interact with.
ChIA-PET workflow:
(Valeria Bastianini)
3. Biochemical determination of binding sequence
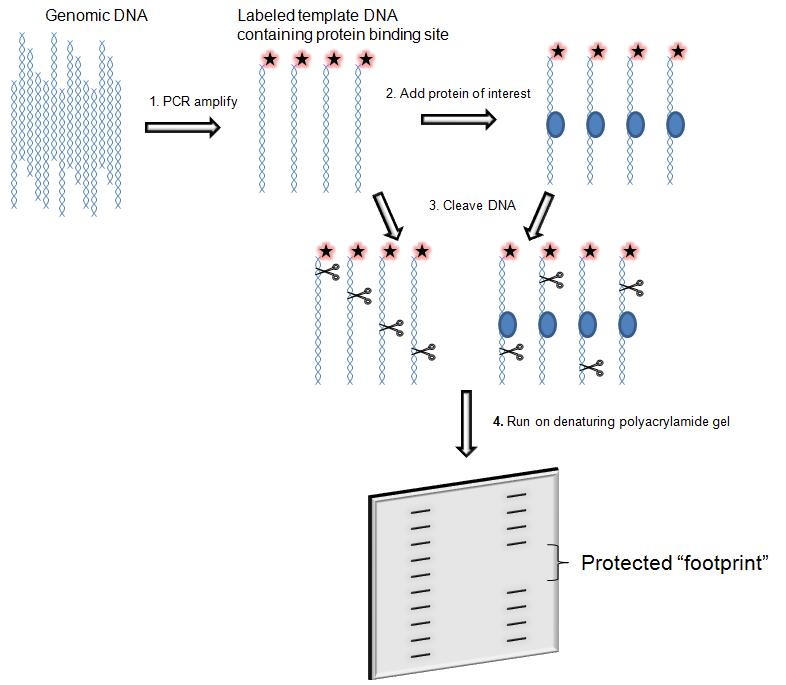
DNase I footprinting
is used to both identifying and characterizing DNA–protein interactions.
The assay consists in the incubation of a DNA fragment of a few hundred base pair labelled with 32-P- radioactively at one end with the proteins suspected to bind. Subsequently the digestion with DNasi I and then the DNA is analysed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography.
The main feature of the assay is that during the digestion the protein bound to DNA protect the DNA from enzymatic cleavage by prevents binding of DNase I in and around its binding site and thus generates a “footprint” in the cleavage ladder that can be seen in electrophoresis's autoradiograph . The distance from the end label to the edges of the footprint represents the position of the protein-binding site on the DNA fragment.
SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment)
It was introduced in 1990.
Selex is a technique to determine the consensus-binding site of a TF without prior information.
The process begins with the synthesis of a very large oligonucleotide library consisting of randomly generated sequences of fixed length flanked by constant 5' and 3' ends that serve as primers (the sequence must be single strand). Library is incubated with immobilized target to allow oligonucleotide-target binding. Subsequently the sequences in the library are exposed to the target ligand (adapter). After the unbound oligonucleotides are washed away usually by affinity chromatography or target capture on paramagnetic beads. Then the bound sequences are eluted using denaturing solutions containing urea and EDTA or by applying high heat and physical force and amplified by PCR. These processes randomized single stranded library generation, incubation, binding, elution and amplification are repeated many time for the selection of sequences.

SELEX variants:
Instead of multiple rounds of binding and amplification, one round of selection at high stringency is sufficient, followed by elution and NGS sequencing.
- Hight-Throughput SELEX: the method utilizes massively parallel single-molecule sequencing technology, which eliminates all cloning steps and results in generation of a very large number of individual sequencing reads. The number of samples that can be analyzed in parallel is increased. The selected fragments can thus be directly sequenced without a ligation or template-switching step, decreasing the risk of sequence bias and DNA contamination. This method was developed for NGS.
- SELEX-Seq: differs from traditional SELEX in two respects the number of selected (bound) DNA oligos characterized (107 selected DNA oligos instead of 102) and the number of rounds of selection performed (one-two rounds)
Indirect technique that identifies regions where the TF binds but doesn't identify the motif sequence.
it is usually followed by statistical analysis
4. ACTIVITY ASSAY FOR TFs (Cristina Demelas)
There are several traditional and well-developed methods for analyzing the activity of transcription factors, such as EMSA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and reporter gene activity assays. Although Western blotting is a good method to detect the content of specific proteins, it can only provide information regarding the total number of the target TFs and so cannot be used to distinguish between active or inactive TFs. The activity of transcription factors are not always correlated with the TF amounts present in the cells; only the active TFs bound to the transcription factor binding site represent instances of gene expression.
a. EMSA
Electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) is the current method used to detect the activity of TFs. Essentially, dsDNA probes containing the TF binding sequences are labeled with the [32P]-radioisotope, and the activity of TFs is determined after electrophoresis based on radioactivity levels.
A
mobility shift assay is electrophoretic separation of a protein–DNA or
protein–RNA mixture on a polyacrylamide or agarose gel for a short period
(about 1.5-2 hr for a 15- to 20-cm gel). The speed at which different molecules
(and combinations) move through the gel is determined by their size and charge,
and to a lesser extent, their shape. This is a retardation assay: a piece of
DNA (a transcription factor binding site in this case) and a protein (purified
transcription factor) are put together in a tube and they assemble. DNA is
labelled: in old papers, it was labelled in a radioactive manner, whereas
today, biotin labelling is the election labelling method. After the formation
of the complex, the preparation is separated on electrophoresis.
The free oligo moves faster than DNA-protein complex, while the complex is retarded: the amount of retardation is comparable with the size of the protein bound to DNA. Protocol steps:
1. Nuclear extracts from cells or tissues;
2. Mix with 32P-labeled ds-oligo;
3. Run on native acrylamide gels.
Looking to an an example of the gel: the control lane (DNA probe without protein present) will contain a single band corresponding to the unbound DNA fragment. However, assuming that the protein is capable of binding to the fragment, the lane with a protein that binds will contain another band that represents the larger, less mobile complex of nucleic acid probe bound to protein which is 'shifted' up on the gel (since it has moved more slowly).
The ratio of bound to unbound nucleic acid on the gel reflects the fraction of free and bound probe molecules as the binding reaction enters the gel.
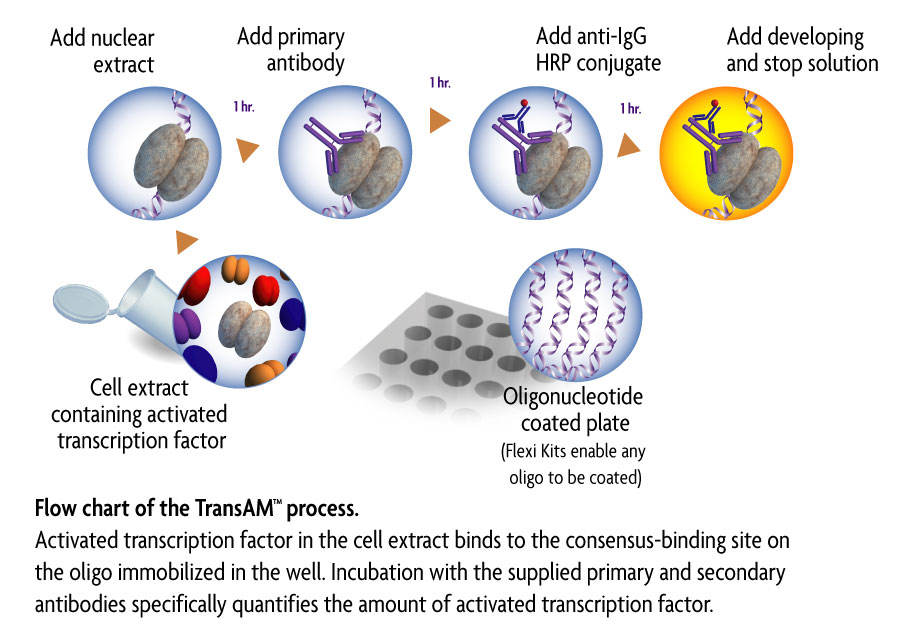
b. ELISA
Colorimetric enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)‐based procedures have been developed to detect specific transcription factor DNA‐binding activity in cell extracts. Up to 96 reactions can be performed in 3 to 4 hr. Extracts are added to the 96‐well plate precoated with a transcription factor DNA‐binding consensus sequence and detected with an antibody specific to the transcription factor of interest. In short, ELISA provides increased speed and throughput, and allows improved sensitivity and convenience over the traditional methods.
c. REPORTER GENE ASSAY
A
reporter gene assay, using transfection of plasmids that contain a
mini-promoter with several copies of TF binding elements followed by reporter
genes (such as luciferase and GFP), can also be used to determine the activity
of TFs in cultured cells. Then transfecting vector in cell type or cell line
where the target transcription factor is expressed. The transfectants generated
by reporter plasmids can be used to detect the changes in the activity of TFs
after treatment with drugs. Therefore, this technique is suitable for use in
high-throughput assays for new drug discovery. However, the efficiency of
transfection of variant cells is unreliable and ranges from susceptible to
resistant. This variable efficiency may lead to false results when the activity
of TFs is compared between different cells.
( ELTON JALIS HERMAN )
Dam-ID ( DNA Adenine Methyltransferase Identification ) :
The identification of transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the genome is critical to understanding gene regulatory networks (GRNs). While ChIP-seq is commonly used to identify TF targets, it requires specific ChIP-grade antibodies and high cell numbers, often limiting its applicability. DNA adenine methyltransferase identification (DamID), developed and widely used in Drosophila, is a distinct technology to investigate protein–DNA interactions. Unlike ChIP-seq, it does not require antibodies, precipitation steps, or chemical protein–DNA crosslinking.
DamID identifies binding sites by expressing the proposed DNA-binding protein as a fusion protein with DNA methyltransferase. Binding of the protein of interest to DNA localizes the methyltransferase in the region of the binding site. Adenosine methylation does not occur naturally in eukaryotes and therefore adenine methylation in any region can be concluded to have been caused by the fusion protein, implying the region is located near a binding site. DamID is an alternate method to ChIP-on-chip or ChIP-seq.
Description and principle of the method :
N6-methyladenine (m6A) is the product of the addition of a methyl group (CH3) at position 6 of the adenine. This modified nucleotide is absent from the vast majority of eukaryotes, but is widespread in bacterial genomes, as part of the restriction modification or DNA repair systems. In Escherichia coli, adenine methylation is catalyzed by the adenine methyltransferase Dam (DNA adenine methyltransferase), which catalyses adenine methylation exclusively in the palindromic sequence GATC. Ectopic expression of Dam in eukaryotic cells leads to methylation of adenine in GATC sequences without any other noticeable side effect.
Based on this, DamID consists in fusing Dam to a protein of interest (usually a protein that interacts with DNA such as transcription factors) or a chromatin component. The protein of interest thus targets Dam to its cognate in vivo binding site, resulting in the methylation of neighboring GATCs. The presence of m6A, coinciding with the binding sites of the proteins of interest, is revealed by methyl PCR.
In methyl PCR, the genome is digested by DpnI, which cuts only methylated GATCs. Double-stranded adapters with a known sequence are then ligated to the ends generated by DpnI. Ligation products are then digested by DpnII. This enzyme cuts non-methylated GATCs, ensuring that only fragments flanked by consecutive methylated GATCs are amplified in the subsequent PCR. A PCR with primers matching the adaptors is then carried out, leading to the specific amplification of genomic fragments flanked by methylated GATCs.
Cell type specific Dam-ID :
A major advantage of DamID over ChIP seq is that profiling of protein binding sites can be assayed in a particular cell type in vivo without requiring the physical separation of a subpopulation of cells. This allows for investigation into developmental or physiological processes in animal models.
Targeted DamID :
The targeted DamID (TaDa) approach uses the phenomenon of ribosome reinitiation to express Dam-fusion proteins at appropriately low levels for DamID (i.e. Dam is non-saturating, thus avoiding toxicity). This construct can be combined with cell-type specific promoters resulting in tissue-specific methylation. This approach can be used to assay transcription factor binding in a cell type of interest or alternatively, dam can be fused to Pol II subunits to determine binding of RNA polymerase and thus infer cell-specific gene expression. Targeted DamID has been demonstrated in Drosophila and mouse cells.
FRT/FLP-out DamID :
[edit]
Cell-specific DamID can also be achieved using recombination mediated excision of a transcriptional terminator cassette upstream of the Dam-fusion protein.The terminator cassette is flanked by FRT recombination sites which can be removed when combined with tissue specific expression of FLP recombinase. Upon removal of the cassette, the Dam-fusion is expressed at low levels under the control of a basal promoter.
Recent Advancements in the Dam-ID method:
An optimized DamID method coupled with next-generation
sequencing (DamID-seq) in mouse cells and demonstrate the identification of the binding sites of two TFs, POU5F1 (also
known as OCT4) and SOX2, in as few as 1000 embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and neural stem cells (NSCs), respectively.
Furthermore, we have applied this technique in vivo for the first time in mammals. POU5F1 DamID-seq in the gastrulating
mouse embryo at 7.5 d post coitum (dpc) successfully identified multiple POU5F1 binding sites proximal to genes involved in
embryo development, neural tube formation, and mesoderm-cardiac tissue development, consistent with the pivotal role of
this TF in post-implantation embryo. This technology paves the way to unprecedented investigation of TF–DNA interactions and GRNs in specific cell types of limited availability in mammals, including in vivo samples.
Things that are modified for optimization :
Genomic DNA was extracted using the Quick-gDNA MicroPrep kit (Zymo Research) and then digested with DpnI, which specifically cuts GAmeTC sequences.
Following adapter ligation, DNA was digested with DpnII (which
specifically cuts nonmethylated GATC sites) before adapter-mediated PCR amplification. The DpnII digestion step was described in
the original protocol to avoid amplification of large fragments that
do not contain Dam/Dam-POI–bound sites but are flanked by the
DpnI-digested GAmeTC sites. Although this step has been excluded
in recent protocols, it is found that the intensity of the Dam-POU5F1 signal
over the Dam-only control was reduced without this DpnII digestion step. POU5F1 DamID has been recently used to validate a DamID-seq protocol in a different study. The data from presented
lower signal-to-noise ratio compared to our data, maybe due to the
lack of DpnII digestion step before PCR amplification in their protocol and/or potentially due to the difficulty in achieving optimal
expression levels of Dam-only/Pou5f1 using viral transduction.
For the amplification of the adapter-ligated DNA fragments, it is found that the KAPA HiFi polymerase provided a better genome
coverage than Advantage to polymerase previously used. Also introduce a qPCR step to determine the
optimal number of PCR cycles for the fragment amplification in
order to minimize amplification biases.
All these steps could be performed in a single tube, and the amplified DNA was then purified using SPRI magnetic beads. The
purified Dam-only/POI target DNA was subjected to library preparation for Illumina sequencing with Tn5 transposition which allowed us to fragment the DNA to the desired size
range (∼250–350 bp) for NGS and to introduce Illumina sequencing–compatible ends in a 5-min reaction. This DamID-seq protocol (from gDNA extraction to NGS library preparation) can be
accomplished in ∼3 d.
POI - protein of interest.
