Antibody production for experimental use
general and practical informations about antibody production
Types of mAbs
Types of mAbs
TYPES OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES:
Following are the different types of monoclonal antibodies:
- Immunotoxins
- Chimeric Immunotoxins
- Humanized antibodies
- CDR grafted antibodies
- Heterconjugate antibodies
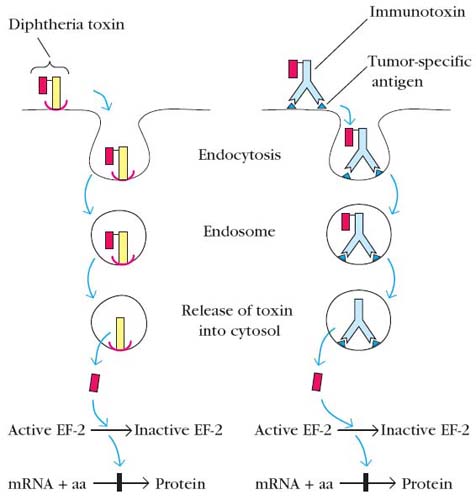
A. Immunotoxins:
It is nothing but the complex of antibodies and toxins like ricin, diphtheria toxin etc., i.e. toxins linked to immunoglobins at their Fc region. Immunotoxins are mainly used against tumors. When Immunotoxins for a particular tumor cells injected, they reached the target cell with the help of antibodies. After their attachment to tumor cells, it is taken up by tumor cells through endocytosis. After this, cellular metabolism interfered with the help of toxins and cells died. Because of the use of monoclonal antibodies, toxins are directed towards specific tumor cells.
B. Chimeric Immunotoxins:
The term chimera used because unlike Immunotoxins, toxin replaces one of the constant region domain of Ig especially carboxy terminal domain of H chain. It can also be used to treat cancers. It is advantageous than Immunotoxins in the sense that it won’t activate complements and consequent inflammatory reaction after binding to the antigens. This is because of the lack of Fc region in chimeric Immunotoxins.
C. Humanized antibodies:
When antibodies from mice injected as anti-tumor agents, they can stimulate immunogenic reactions against them in the host. This can be avoided to certain extent using humanized antibodies. Humanized antibodies contain constant region of both L and H chain derived from humans and variable regions derived from mice. It is named so because of the presence of human gene coding regions. It can be used as diagnostic tool also.
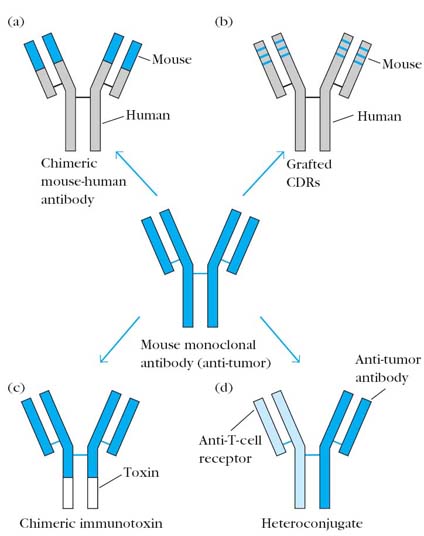
D. CDR grafted Antibodies:
It is the modified form of humanized antibodies i.e. hypervariable region of both light and heavy chains variable region gene only derived from mice. The remaining genes derived from human. It is used against cancer and it also act as immunosuppressor. Usually in such cases, antibodies are directed against CD3 or CD4 components. Because once these components blocked, activation of cell mediated immunity affected.
E. Heterconjugate antibodies:
The word hetero means that antibodies with different specificity i.e. different Paratopes having different specificity in single antibody. This type of antibody specifically used to treat cancer. In this case, one paratope of antibody directed against tumor cells whereas other paratope is directed against cytotoxic cells usually Tc cells. These antibodies bring effective cytotoxic cells close to tumor cells, so that they are easily lysed by cytotoxic mechanisms.
ABZYMES:
Antibodies with enzymatic activity are referred as abzymes. They are otherwise called as catalytic antibodies. The binding of an antibody to its antigen is similar in many ways to the binding of an enzyme to its substrate. In both cases the binding involves weak, non-covalent interactions and exhibits high specificity and often high affinity. What distinguishes an antibody-antigen interaction from an enzyme- substrate interaction is that the antibody does not alter the antigen, whereas the enzyme catalyzes a chemical change in its substrate. However, like enzymes, antibodies of appropriate specificity can stabilize the transition state of a bound substrate, thus reducing the activation energy for chemical modification of the substrate. The similarities between antigen-antibody interactions and enzyme-substrate interactions raised the question of whether some antibodies could behave like enzymes and catalyze chemical reactions. To investigate this possibility, a hapten-carrier complex was synthesized in which the hapten structurally resembled the transition state of an ester undergoing hydrolysis. Spleen cells from mice immunized with this transition state analogue were fused with myeloma cells to generate monoclonal anti-hapten monoclonal antibodies. When these monoclonal antibodies were incubated with an ester substrate, some of them accelerated hydrolysis by about 1000-fold; that is, they acted like the enzyme that normally catalyzes the substrate’s hydrolysis. The catalytic activity of these antibodies was highly specific; that is, they hydrolyzed only esters whose transition-state structure closely resembled the transition state analogue used as a hapten in the immunizing conjugate.
