By agreement with the publisher, this book is accessible by the search feature, but cannot be browsed.
Antibodies are proteins, and proteins are encoded by genes. Antibody diversity therefore poses a special genetic problem: how can an animal make more antibodies than there are genes in its genome? (The human genome, for example, contains fewer than 50,000 genes.) This problem is not quite as formidable as it might first appear. Recall that the variable regions of both the light and heavy chains of antibodies usually form the antigen-binding site. Thus, an animal with 1000 genes encoding light chains and 1000 genes encoding heavy chains could, in principle, combine their products in 1000 × 1000 different ways to make 106 different antigen-binding sites (although, in reality, not every light chain can combine with every heavy chain to make an antigen-binding site). Nonetheless, the mammalianimmune system has evolved unique genetic mechanisms that enable it to generate an almost unlimited number of different light and heavy chains in a remarkably economical way, by joining separate gene segments together before they are transcribed. Birds and fish use very different strategies for diversifying antibodies, and even sheep and rabbits use somewhat different strategies from mice and humans. We shall confine our discussion to the mechanisms used by mice and humans.
We begin this section by discussing the mechanisms that B cells use to produce antibodies with an enormous diversity of antigen-binding sites. We then consider how a B cell can alter the tail region of the antibody it makes, while keeping the antigen-binding site unchanged. This ability allows the B cell to switch from making membrane-bound antibody to making secreted antibody, or from making one class of antibody to making another, all without changing the antigen-specificity of the antibody.
Antibody Genes Are Assembled From Separate Gene Segments During B Cell Development
The first direct evidence that DNA is rearranged during B cell development came in the 1970s from experiments in which molecular biologists compared DNA from early mouse embryos, which do not make antibodies, with the DNA of a mouse B cell tumor, which makes a single species of antibody molecule. The specific variable (V)-region and constant (C)-region coding sequences that the tumor cells used were present on the same DNA restriction fragment in the tumor cells but on two different restriction fragments in the embryos. This showed that the DNA sequences encoding an antibody molecule are rearranged at some stage in B cell development (Figure 24-36).
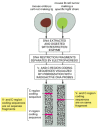
Figure 24-36
Drawing of an experiment that directly demonstrates that DNA is rearranged during B cell development. The B cell tumor arose from a single B cell and therefore makes a single species of antibody molecule. The two radioactive DNA probes used are specific (more...)
We now know that each type of antibody chain--κ light chains, λ light chains, and heavy chains--has a separate pool of gene segments and exons from which a single polypeptide chain is eventually synthesized. Each pool is on a different chromosome and contains a large number of gene segments encoding the V region of an antibody chain and, as we saw in Figure 24-33, a smaller number of exons encoding the C region. During the development of a B cell, a complete coding sequence for each of the two antibody chains to be synthesized is assembled by site-specific genetic recombination (discussed in Chapter 5). In addition to bringing together the separate gene segments and the C-region exons of the antibody gene, these rearrangements also activate transcription from the gene promoter through changes in the relative positions of the enhancers and silencers acting on the promoter. Thus, a complete antibody chain can be synthesized only after the DNA has been rearranged. As we shall see, the process of joining gene segments contributes to the diversity of antigen-binding sites in several ways.
Each Variable Region Is Encoded by More Than One Gene Segment
When genomic DNA sequences encoding V and C regions were first analyzed, it was found that a single region of DNA encodes the C region of an antibody chain (see Figure 24-33), but two or more regions of DNA have to be assembled to encode each V region. Each light-chain V region is encoded by a DNA sequence assembled from twogene segments--a long V gene segment and a short joining, or J gene segment (not to be confused with the protein J chain (see Figure 24-23), which is encoded elsewhere in the genome). Figure 24-37 illustrates the genetic mechanisms involved in producing a human κ light-chain polypeptide from a C-region exon and separate V and Jgene segments.
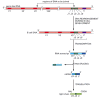
Figure 24-37
The V-J joining process involved in making a human κ light chain. In the "germ-line” DNA (where the antibody genes are not being expressed and are therefore not rearranged), the cluster of five J gene segments is separated from(more...)
Each heavy-chain V region is encoded by a DNA sequence assembled from three gene segments--a V segment, a Jsegment, and a diversity segment, or D gene segment. Figure 24-38 shows the number and organization of the gene segments used in making human heavy chains.
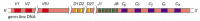
Figure 24-38
The human heavy-chain gene-segment pool. There are 51 V segments, 27 Dsegments, 6 J segments, and an ordered cluster of C-region exons, each cluster encoding a different class of heavy chain. The D segment (and part of the Jsegment) encodes amino acids (more...)
The large number of inherited V, J, and D gene segments available for encoding antibody chains makes a substantial contribution on its own to antibody diversity, but the combinatorial joining of these segments (called combinatorial diversification) greatly increases this contribution. Any of the 40 V segments in the human κ light-chain gene-segment pool, for example, can be joined to any of the 5 J segments (see Figure 24-37), so that at least 200 (40 × 5) different κ-chain V regions can be encoded by this pool. Similarly, any of the 51 V segments in the human heavy-chain pool can be joined to any of the 6 J segments and any of the 27 D segments to encode at least 8262 (51 × 6 × 27) different heavy-chain V regions.
The combinatorial diversification resulting from the assembly of different combinations of inherited V, J, and D genesegments just discussed is an important mechanism for diversifying the antigen-binding sites of antibodies. By this mechanism alone, a human can produce 287 different VL regions (200 κ and 116 λ) and 8262 different VH regions. In principle, these could then be combined to make about 2.6 × 106 (316 × 8262) different antigen-binding sites. In addition, as we discuss next, the joining mechanism itself greatly increases this number of possibilities (probably more than 108-fold), making it much greater than the total number of B cells (about 1012) in a human.
Imprecise Joining of Gene Segments Greatly Increases the Diversity of V Regions
During B cell development, the V and J gene segments (for the light chain) and the V, D, and J gene segments (for the heavy chain) are joined together to form a functional VL- or VH-region coding sequence by a process of site-specific recombination called V(D)J joining.Conserved DNA sequences flank each gene segment and serve as recognition sites for the joining process, ensuring that only appropriate gene segments recombine. Thus, for example, a V segment will always join to a J or D segment but not to another V segment. Joining is mediated by an enzyme complex called the V(D)J recombinase. This complex contains two proteins that are specific to developing lymphocytes, as well as enzymes that help repair damaged DNA in all our cells.
The lymphocyte-specific proteins of the V(D)J recombinase are encoded by two closely linked genes called rag-1 andrag-2 (rag = recombination activating genes). The RAG proteins introduce double-strand breaks at the flankingDNA sequences, and this is followed by a rejoining process that is mediated by both the RAG proteins and the enzymes involved in general DNA double-strand repair (discussed in Chapter 5). Thus, if both rag genes are artificially expressed in a fibroblast, the fibroblast is now able to rearrange experimentally introduced antibody genesegments just as a developing B cell normally does. Moreover, individuals who are deficient in either rag gene or in one of the general repair enzymes are highly susceptible to infection because they are unable to carry out V(D)Jjoining and consequently do not have functional B or T cells. (T cells use the same recombinase to assemble the gene segments that encode their antigen-specific receptors.)
In most cases of site-specific recombination, DNA joining is precise. But during the joining of antibody (and T cellreceptor) gene segments, a variable number of nucleotides are often lost from the ends of the recombining gene segments, and one or more randomly chosen nucleotides may also be inserted. This random loss and gain of nucleotides at joining sites is called junctional diversification, and it enormously increases the diversity of V-region coding sequences created by recombination, specifically in the third hypervariable region. This increased diversification comes at a price, however. In many cases, it will result in a shift in the reading frame that produces a nonfunctional gene. Because roughly two in every three rearrangements are "nonproductive” in this way, many developing B cells never make a functional antibody molecule and consequently die in the bone marrow. B cellsmaking functional antibody molecules that bind strongly to self antigens in the bone marrow are stimulated to re-express the RAG proteins and undergo a second round of V(D)J rearrangements, thereby changing the specificity of the cell-surface antibody they make--a process referred to as receptor editing. Self-reactive B cells that fail to change their specificity in this way are eliminated through the process of clonal deletion (see Figure 24-13).
Antigen-Driven Somatic Hypermutation Fine-Tunes Antibody Responses
As mentioned earlier, with the passage of time after immunization, there is usually a progressive increase in the affinity of the antibodies produced against the immunizing antigen. This phenomenon, known as affinity maturation, is due to the accumulation of point mutations specifically in both heavy-chain and light-chain V-region coding sequences. The mutations occur long after the coding regions have been assembled, when B cells are stimulated by antigen and helper T cells to generate memory cells in a lymphoid follicle in a peripheral lymphoid organ (see Figure 24-16). They occur at the rate of about one per V-region coding sequence per cell generation. Because this is about a million times greater than the spontaneous mutation rate in other genes, the process is called somatic hypermutation. The molecular mechanism is still uncertain, but it is believed to involve some form of error-prone DNA repair process targeted to the rearranged V-region coding sequence by specific regions of DNA brought together by V(D)J joining. Surprisingly, an enzyme involved in RNA editing (discussed in Chapter 7) is required, but its function in the hypermutation process is unknown.
Only a small minority of the altered antigen receptors generated by hypermutation have an increased affinity for the antigen. The few B cells expressing these higher-affinity receptors, however, are preferentially stimulated by the antigen to survive and proliferate, whereas most other B cells die by apoptosis. Thus, as a result of repeated cycles of somatic hypermutation, followed by antigen-driven proliferation of selected clones of memory B cells, antibodies of increasingly higher affinity become abundant during an immune response, providing progressively better protection against the pathogen.
The main mechanisms of antibody diversification are summarized in Figure 24-39.
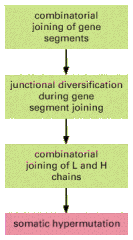
Figure 24-39
The four main mechanisms of antibody diversification. Those shaded in greenoccur during B cell development in the bone marrow (or fetal liver), while the mechanism shaded in red occurs when B cells are stimulated by foreign antigen and helper T cells (more...)
The Control of V(D)J Joining Ensures That B Cells Are Monospecific
As the clonal selection theory predicts, B cells are monospecific. That is, all the antibodies that any one B cellproduces have identical antigen-binding sites. This property enables antibodies to cross-link antigens into large aggregates, thereby promoting antigen elimination (see Figure 24-19). It also means that an activated B cell secretes antibodies with the same specificity as that of the membrane-bound antibody on the B cell that was originally stimulated.
The requirement of monospecificity means that each B cell can make only one type of VL region and one type of VHregion. Since B cells, like most other somatic cells, are diploid, each cell has six gene-segment pools encoding antibody chains: two heavy-chain pools (one from each parent) and four light-chain pools (one κ and one λ from each parent). If DNA rearrangements occurred independently in each heavy-chain pool and each light-chain pool, a singlecell could make up to eight different antibodies, each with a different antigen-binding site.
In fact, however, each B cell uses only two of the six gene-segment pools: one of the two heavy-chain pools and one of the four light-chain pools. Thus, each B cell must choose not only between its κ and λ light-chain pools, but also between its maternal and paternal light-chain and heavy-chain pools. This second choice is called allelic exclusion, and it also occurs in the expression of genes that encode T cell receptors. For most other proteins that are encoded by autosomal genes, both maternal and paternal genes in a cell are expressed about equally.
Allelic exclusion and κ versus λ light-chain choice during B cell development depend on negative feedback regulation of the V(D)J joining process. A functional rearrangement in one gene-segment pool suppresses rearrangements in all remaining pools that encode the same type of polypeptide chain (Figure 24-40). In B cell clones isolated from transgenic mice expressing a rearranged μ-chain gene, for example, the rearrangement of endogenous heavy-chain genes is usually suppressed. Comparable results have been obtained for light chains. The suppression does not occur if the product of the rearranged gene fails to assemble into a receptor that inserts into the plasma membrane. It has therefore been proposed that either the receptor assembly process itself or extracellular signals that act on the receptor are involved in the suppression of further gene rearrangements.
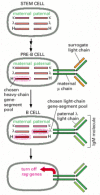
Figure 24-40
Antibody gene-pool selection in B cell development. To produce antibodies with only one type of antigen-binding site, a developing B cell must use only one L-chain gene-segment pool and one H-chain pool. Although the choice between maternal and paternal (more...)
Although no biological differences between the constant regions of κ and λ light chains have been discovered, there is an advantage in having two separate pools of gene segments encoding light chain variable regions. Having two separate pools increases the chance that a pre-B cell that has successfully assembled a VH-region coding sequence will go on to assemble successfully a VL-region coding sequence to become a B cell. This chance is further increased because, before a developing pre-B cell produces ordinary light chains, it makes surrogate light chains (see Figure 24-22), which assemble with μ heavy chains. The resulting receptors are displayed on the cell surface and allow the cellto proliferate, producing large numbers of progeny cells, some of which are likely to succeed in producing bona fide light chains.
When Activated by Antigen, a B Cell Switches From Making a Membrane-Bound Antibody to Making a Secreted Form of the Same Antibody
We now turn from the genetic mechanisms that determine the antigen-binding site of an antibody to those that determine its biological properties--that is, those that determine what form of heavy-chain constant region is synthesized. The choice of the particular gene segments that encode the antigen-binding site is a commitment for the life of a B cell and its progeny, but the type of CH region that is made changes during B cell development. The changes are of two types: changes from a membrane-bound form to a secreted form of the same CH region and changes in the class of the CH region made.
All classes of antibody can be made in a membrane-bound form, as well as in a soluble, secreted form. The membrane-bound form serves as an antigen receptor on the B cell surface, while the soluble form is made only after the cell is activated by antigen to become an antibody-secreting effector cell (see Figure 24-17). The sole difference between the two forms resides in the C-terminus of the heavy chain. The heavy chains of membrane-bound antibody molecules have a hydrophobic C-terminus, which anchors them in the lipid bilayer of the B cell's plasma membrane. The heavy chains of secreted antibody molecules, by contrast, have instead a hydrophilic C-terminus, which allows them to escape from the cell. The switch in the character of the antibody molecules made occurs because the activation of B cells by antigen (and helper T cells) induces a change in the way in which the H-chain RNAtranscripts are made and processed in the nucleus (see Figure 7-93).
B Cells Can Switch the Class of Antibody They Make
During B cell development, many B cells switch from making one class of antibody to making another--a process called class switching. All B cells begin their antibody-synthesizing lives by making IgM molecules and inserting them into the plasma membrane as receptors for antigen. After the B cells leave the bone marrow, but before they interact with antigen, they switch and make both IgM and IgD molecules as membrane-bound antigen receptors, both with the same antigen-binding sites (see Figure 24-22). On stimulation by antigen and helper T cells, some of thesecells are activated to secrete IgM antibodies, which dominate the primary antibody response. Later in the immune response, the combination of antigen and the cytokines that helper T cells secrete induce many B cells to switch to making IgG, IgE, or IgA antibodies. These cells generate both memory cells that express the corresponding classes of antibody molecules on their surface and effector cells that secrete the antibodies. The IgG, IgE, and IgA molecules are collectively referred to as secondary classes of antibodies, both because they are produced only after antigen stimulation and because they dominate secondary antibody responses. As we saw earlier, each different class of antibody is specialized to attack microbes in different ways and in different sites.
The constant region of an antibody heavy chain determines the class of the antibody. Thus, the ability of B cells to switch the class of antibody they make without changing the antigen-binding site implies that the same assembled VH-region coding sequence (which specifies the antigen-binding part of the heavy chain) can sequentially associate with different CH-coding sequences. This has important functional implications. It means that, in an individual animal, a particular antigen-binding site that has been selected by environmental antigens can be distributed among the various classes of antibodies, thereby acquiring the different biological properties of each class.
When a B cell switches from making IgM and IgD to one of the secondary classes of antibody, an irreversible change at the DNA level occurs--a process called class switch recombination. It entails deletion of all the CH-coding sequences between the assembled VDJ-coding sequence and the particular CH-coding sequence that the cell is destined to express (Figure 24-41). Switch recombination differs from V(D)J joining in several ways: (1) it involves noncoding sequences only and therefore leaves the coding sequence unaffected; (2) it uses different flanking recombination sequences and different enzymes; (3) it happens after antigen stimulation; and (4) it is dependent on helper T cells.
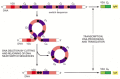
Figure 24-41
An example of the DNA rearrangement that occurs in class switch recombination. A B cell making an IgM antibody from an assembled VDJDNA sequence is stimulated by antigen and the cytokines made by helper Tcells to switch to making an IgA antibody. In (more...)
Summary
Antibodies are produced from three pools of gene segments and exons. One pool encodes κ light chains, one encodes λ light chains, and one encodes heavy chains. In each pool, separate gene segments that code for different parts of thevariable region of the light or heavy chains are brought together by site-specific recombination during B celldevelopment. The light-chain pools contain one or more constant- (C-) region exons and sets of variable (V) and joining (J) gene segments. The heavy-chain pool contains sets of C-region exons and sets of V, diversity (D), and J gene segments.
To make an antibody molecule, a VL gene segment recombines with a JL gene segment to produce a DNA sequence coding for the V region of a light chain, and a VH gene segment recombines with a D and a JH gene segment to produce a DNA sequence coding for the V region of a heavy chain. Each of the assembled V-region coding sequences is then cotranscribed with the appropriate C-region sequence to produce an RNA molecule that codes for the complete polypeptide chain. Cells making functional heavy and light chains turn off the V(D)J joining process to ensure that each B cell makes only one species of antigen-binding site.
By randomly combining inherited gene segments that code for VL and VH regions, humans can make hundreds of different light chains and thousands of different heavy chains. Because the antigen-binding site is formed where the hypervariable loops of the VL and VH come together in the final antibody, the heavy and light chains can pair to form antibodies with millions of different antigen-binding sites. This number is enormously increased by the loss and gain of nucleotides at the site of gene-segment joining, as well as by somatic mutations that occur with very high frequency in the assembled V-region coding sequences after stimulation by antigen and helper T cells.
All B cells initially make IgM antibodies, and most then make IgD as well. Later many switch and make antibodies of other classes but with the same antigen-binding site as the original IgM and IgD antibodies. Such class switchingdepends on antigen stimulation and helper T cells, and it allows the same antigen-binding sites to be distributed among antibodies with varied biological properties.
