Antibody production for experimental use
general and practical informations about antibody production
polyclonal/monoclonal
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION
Antibodies having single specificity produced from a single clone of B cell are referred as Mono clonal antibodies (MAbs). In 1975, Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein devised a method for preparing monoclonal antibody, which quickly became one of immunology’s key technologies. The significance of the work by Köhler and Milstein was acknowledged when each was awarded a Nobel Prize.
CONVENTIONAL METHOD OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY PRODUCTION:
Group of antibodies having different specificity produced from different clone of B cell is referred as polyclonal antibodies. Antigens with multi-epitopes injected into mice. After an incubation period serum is isolated from mice. It will contain antibodies against different epitopes and they are also produced from different clone of cells. Serums with antibodies are known as antiserum which is produced against an injected antigen like antitoxin which is nothing but antibody produced against toxins.
Antigens with multivalent epitope injected into mice. After incubation period B cells are isolated. They are hybridized with myeloma cells with the help of fusogens different types of B cells are separated. Antibodies from each type act as mono clonal antibodies.
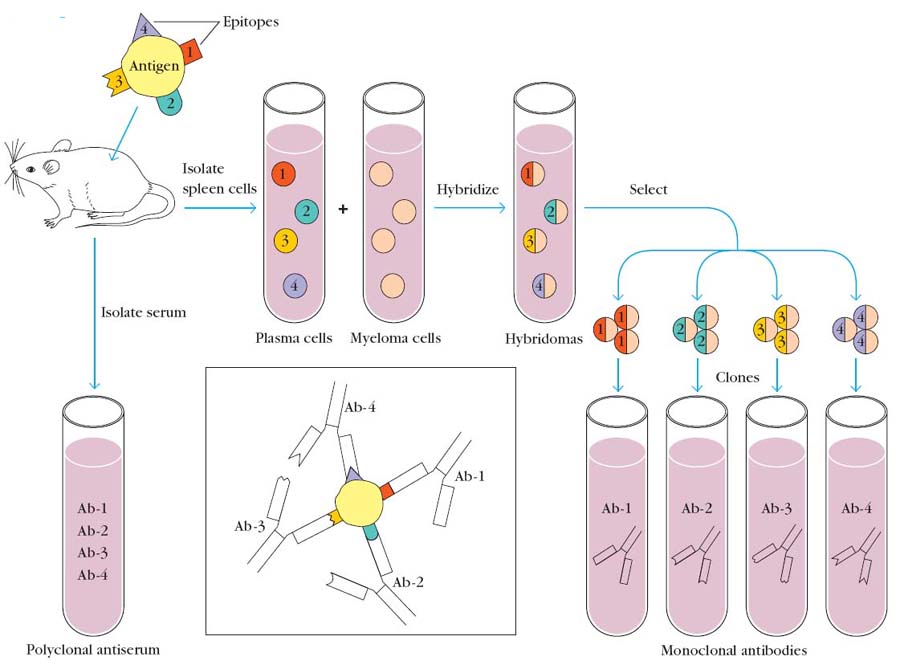
Monoclonal antibodies are produced mainly by hybridoma technology.
HYBRIDOMA TECHNOLOGY:
It refers to the production of hybridoma cells by a technology. In this technology, cells of interest hybridized with cancer cells. The aim of this technology is to provide immortality to the cells of interest.
When cells of interest fused with cancer cells with the help of fusogens like sendaivirus or polyethylene glycol (PEG), first cytoplasmic membrane of two cells are fused to form heterokaryon i.e. cells with two different nucleuses. Then the two nucleuses combined to form cybrid or hybrid cells. Hybrid cells contain combination of both cell nuclear materials but maintaining species usual chromosomal number by loss of extra chromosome. In cybrid cells genetic material of either of the cell maintained completely and the other one is lost completely i.e. cybrid cells are hybrids considering the cytoplasmic component.
Of the three possibility of cells like unfused cells, hybridoma cells and cybrid cells, hybridoma cells selected by using HAT (Hypoxanthine Aminopterin Thymidine) medium.
